1. Materials#
concreteproperties requires material properties to be defined for the concrete and steel components of the reinforced concrete section. Any number of different material properties can be used for a single cross-section. For example, higher strength precast sections can be topped with lower grade in-situ slabs, and high tensile steel can be used in combination with normal grade reinforcing steel.
The structural behaviour of materials is described by Stress-Strain Profiles.
Note
In concreteproperties, a positive sign is given to compressive forces, stresses and strains, while a negative sign is given to tensile forces, stresses and strains.
1.1. Material Classes#
concreteproperties ships with material objects describing the structural behaviour of
both concrete and steel. The generic Material
class can be used to describe the behaviour of any other material.
By default, all geometries in concreteproperties are meshed to capture strain
variation across the section. However, for smaller geometries (such as reinforcement),
concreteproperties can treat the area as having a constant strain with a lumped mass,
which increases the performance of the analysis with almost no loss in fidelity. The
meshing can be switched off by setting the attribute meshed=False.
The SteelBar class has meshing disabled by default
and should be used when defining steel reinforcement. On the other hand, the
Steel class is meshed by default so should be used
when defining larger sections such as strucutral steel sections used in composite
sections.
1.1.1. Material#
- class Material(name, density, stress_strain_profile, colour, meshed)[source]
Generic class for a concreteproperties material.
- Parameters
name (
str) – Material namedensity (
float) – Material density (mass per unit volume)stress_strain_profile (
StressStrainProfile) – Material stress-strain profilecolour (
str) – Colour of the material for renderingmeshed (
bool) – If set to True, the entire material region is meshed; if set to False, the material region is treated as a lumped circular mass at its centroid
1.1.2. Concrete#
- class Concrete(name, density, stress_strain_profile, colour, ultimate_stress_strain_profile, flexural_tensile_strength)[source]
Class for a concrete material.
- Parameters
name (
str) – Concrete material namedensity (
float) – Concrete density (mass per unit volume)stress_strain_profile (
ConcreteServiceProfile) – Service concrete stress-strain profileultimate_stress_strain_profile (
ConcreteUltimateProfile) – Ultimate concrete stress-strain profileflexural_tensile_strength (
float) – Absolute value of the concrete flexural tensile strengthcolour (
str) – Colour of the material for rendering
1.1.3. Steel#
- class Steel(name, density, stress_strain_profile, colour)[source]
Class for a steel material with the entire region meshed to allow for strain variation across the section, e.g. structural steel profiles.
- Parameters
name (
str) – Steel material namedensity (
float) – Steel density (mass per unit volume)stress_strain_profile (
StressStrainProfile) – Steel stress-strain profilecolour (
str) – Colour of the material for rendering
1.1.4. SteelBar#
- class SteelBar(name, density, stress_strain_profile, colour)[source]
Class for a steel bar material, treated as a lumped circular mass with a constant strain.
- Parameters
name (
str) – Steel bar material namedensity (
float) – Steel bar density (mass per unit volume)stress_strain_profile (
StressStrainProfile) – Steel bar stress-strain profilecolour (
str) – Colour of the material for rendering
1.2. Stress-Strain Profiles#
concreteproperties uses stress-strain profiles to define material behaviour for both
service and ultimate analyses. A Concrete object
requires both a service stress-strain profile (calculation of area properties,
moment-curvature analysis, elastic and service stress analysis) and an ultimate
stress-strain profile (ultimate bending capacity, moment interaction diagram, biaxial
bending diagram, ultimate stress analysis). All other material objects only requires one
stress-strain profile which is used for both service and ultimate analyses.
Note
Stress values are interpolated from stresses and strains supplied to the profile. If the strain is outside of the range of the stress-strain profile, the stress is extrapolated based off the closest two points of the stress-strain profile.
- class StressStrainProfile(strains, stresses)[source]
Abstract base class for a material stress-strain profile.
Implements a piecewise linear stress-strain profile. Positive stresses & strains are compression.
- Parameters
strains (
List[float]) – List of strains (must be increasing or equal)stresses (
List[float]) – List of stresses
- print_properties(fmt='8.6e')[source]
Prints the stress-strain profile properties to the terminal.
- Parameters
fmt (
str, default:'8.6e') – Number format
- plot_stress_strain(title='Stress-Strain Profile', fmt='o-', **kwargs)[source]
Plots the stress-strain profile.
- Parameters
title (
str, default:'Stress-Strain Profile') – Plot titlefmt (
str, default:'o-') – Plot format stringkwargs – Passed to
plotting_context()
- Returns
Axes– Matplotlib axes object
1.2.1. Concrete Service Stress-Strain Profiles#
Note
Unless assigned in the class constructor, the elastic_modulus of the concrete is
determined by the initial compressive slope of the stress-strain profile. This
elastic_modulus is used in the calculation of area properties and elastic stress
analysis.
1.2.1.1. Generic Concrete Service Profile#
- class ConcreteServiceProfile(strains, stresses, ultimate_strain)[source]
Bases:
StressStrainProfileAbstract class for a concrete service stress-strain profile.
- Parameters
strains (
List[float]) – List of strains (must be increasing or equal)stresses (
List[float]) – List of stressesultimate_strain (
float) – Concrete strain at failure
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import ConcreteServiceProfile
ConcreteServiceProfile(
strains=[-5 / 35e3, -4 / 35e3, -3 / 35e3, 0, 40 / 35e3, 0.003],
stresses=[0, 0, -3, 0, 40, 40],
ultimate_strain=0.003,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
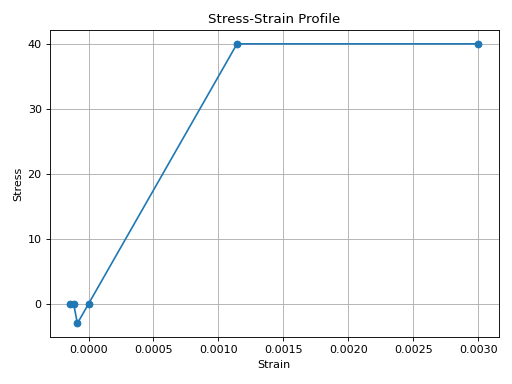
ConcreteServiceProfile Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.1.2. Linear Concrete Service Profile#
- class ConcreteLinear(elastic_modulus, ultimate_strain=1)[source]
Bases:
ConcreteServiceProfileClass for a symmetric linear stress-strain profile.
- Parameters
elastic_modulus (
float) – Elastic modulus of the stress-strain profileultimate_strain (
float, default:1) – Concrete strain at failure
Warning
This profile is not intended to be used in conjunction with a
moment_curvature_analysis()
as the concrete can resist large tensile stresses without fracture.
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import ConcreteLinear
ConcreteLinear(elastic_modulus=35e3).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
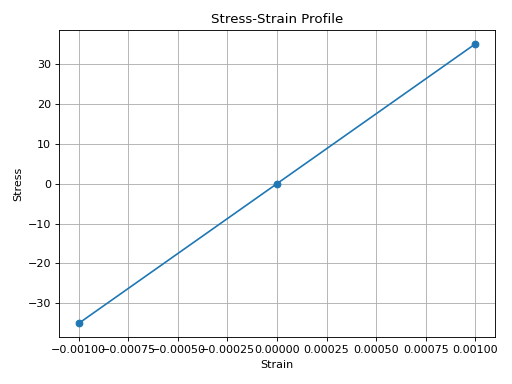
ConcreteLinear Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.1.3. Linear Concrete (No Tension) Service Profile#
- class ConcreteLinearNoTension(elastic_modulus, ultimate_strain=1, compressive_strength=None)[source]
Bases:
ConcreteServiceProfileClass for a linear stress-strain profile with no tensile strength.
- Parameters
elastic_modulus (
float) – Elastic modulus of the stress-strain profileultimate_strain (
float, default:1) – Concrete strain at failurecompressive_strength (
Optional[float], default:None) – Compressive strength of the concrete
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import ConcreteLinearNoTension
ConcreteLinearNoTension(elastic_modulus=35e3).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
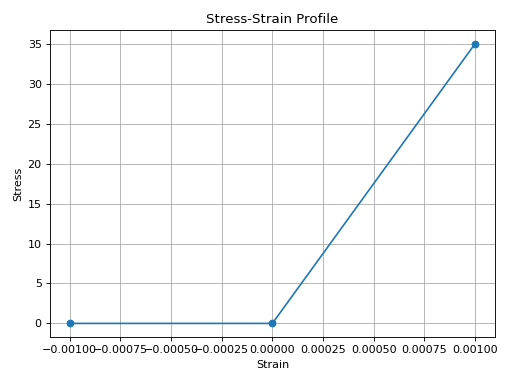
ConcreteLinearNoTension Stress-Strain Profile#
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import ConcreteLinearNoTension
ConcreteLinearNoTension(
elastic_modulus=35e3,
ultimate_strain=0.003,
compressive_strength=40,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
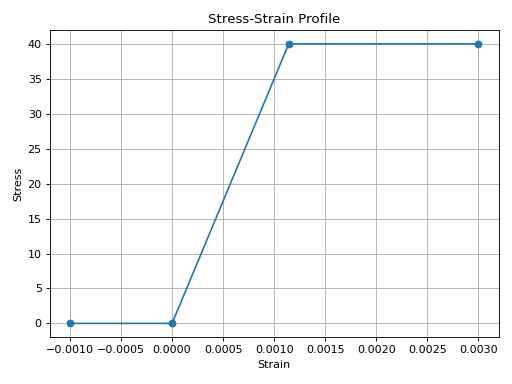
ConcreteLinearNoTension Stress-Strain Profile with Compressive Strength#
1.2.1.4. Eurocode Non-Linear Concrete Service Profile#
- class EurocodeNonLinear(elastic_modulus, ultimate_strain, compressive_strength, compressive_strain, tensile_strength, tension_softening_stiffness, n_points_1=10, n_points_2=3)[source]
Bases:
ConcreteServiceProfileClass for a non-linear stress-strain relationship to EC2.
Tension is modelled with a symmetric
elastic_modulusuntil failure attensile_strength, after which the tensile stress reduces according to thetension_softening_stiffness.- Parameters
elastic_modulus (
float) – Concrete elastic modulus (\(E_{cm}\))ultimate_strain (
float) – Concrete strain at failure (\(\epsilon_{cu1}\))compressive_strength (
float) – Concrete compressive strength (\(f_{cm}\))compressive_strain (
float) – Strain at which the concrete stress equals the compressive strength (\(\epsilon_{c1}\))tensile_strength (
float) – Concrete tensile strengthtension_softening_stiffness (
float) – Slope of the linear tension softening branchn_points_1 (
int, default:10) – Number of points to discretise the curve prior to the peak stressn_points_2 (
int, default:3) – Number of points to discretise the curve after the peak stress
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import EurocodeNonLinear
EurocodeNonLinear(
elastic_modulus=35e3,
ultimate_strain=0.0035,
compressive_strength=40,
compressive_strain=0.0023,
tensile_strength=3.5,
tension_softening_stiffness=7e3,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
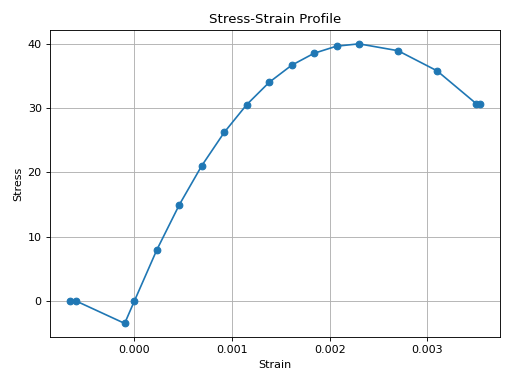
EurocodeNonLinear Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.2. Concrete Ultimate Stress-Strain Profiles#
Note
Unless assigned in the class constructor, the ultimate_strain of the concrete is
taken as the largest compressive strain in the stress-strain profile. This
ultimate_strain defines the curvature and strain profile used in ultimate
analyses.
Warning
concreteproperties currently only supports a single unique ultimate_strain to be
used for a given ConcreteSection. While
multiple concrete materials, with differing stress-strain profiles, can be
used within a given ConcreteSection, the
ultimate analysis will use the smallest value of the ultimate_strain amongst the
various concrete materials to define the strain profile at ultimate.
1.2.2.1. Generic Concrete Ultimate Profile#
- class ConcreteUltimateProfile(strains, stresses, compressive_strength)[source]
Bases:
StressStrainProfileAbstract class for a concrete ultimate stress-strain profile.
- Parameters
strains (
List[float]) – List of strains (must be increasing or equal)stresses (
List[float]) – List of stressescompressive_strength (
float) – Concrete compressive strength
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import ConcreteUltimateProfile
ConcreteUltimateProfile(
strains=[-20 / 30e3, 0, 20 / 30e3, 30 / 25e3, 40 / 20e3, 0.003],
stresses=[0, 0, 20, 30, 40, 40],
compressive_strength=32,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
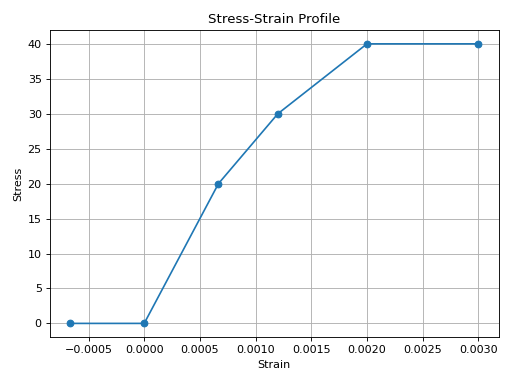
ConcreteUltimateProfile Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.2.2. Rectangular Stress Block#
- class RectangularStressBlock(compressive_strength, alpha, gamma, ultimate_strain)[source]
Bases:
ConcreteUltimateProfileClass for a rectangular stress block.
- Parameters
compressive_strength (
float) – Concrete compressive strengthalpha (
float) – Factor that modifies the concrete compressive strengthgamma (
float) – Factor that modifies the depth of the stress blockultimate_strain (
float) – Concrete strain at failure
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import RectangularStressBlock
RectangularStressBlock(
compressive_strength=40,
alpha=0.85,
gamma=0.77,
ultimate_strain=0.003,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
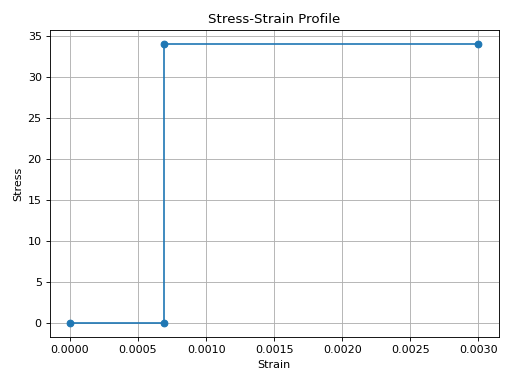
RectangularStressBlock Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.2.3. Bilinear Ultimate Profile#
- class BilinearStressStrain(compressive_strength, compressive_strain, ultimate_strain)[source]
Bases:
ConcreteUltimateProfileClass for a bilinear stress-strain relationship.
- Parameters
compressive_strength (
float) – Concrete compressive strengthcompressive_strain (
float) – Strain at which the concrete stress equals the compressive strengthultimate_strain (
float) – Concrete strain at failure
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import BilinearStressStrain
BilinearStressStrain(
compressive_strength=40,
compressive_strain=0.00175,
ultimate_strain=0.0035,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
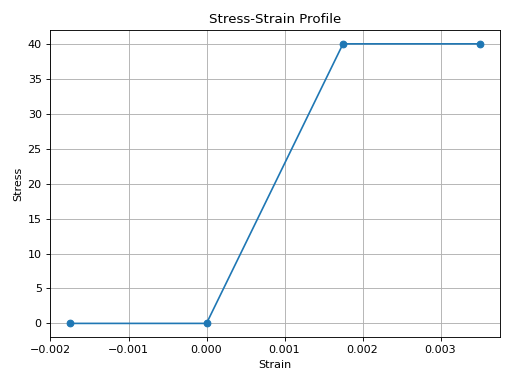
BilinearStressStrain Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.2.4. Eurocode Parabolic Ultimate Profile#
- class EurocodeParabolicUltimate(compressive_strength, compressive_strain, ultimate_strain, n, n_points=10)[source]
Bases:
ConcreteUltimateProfileClass for an ultimate parabolic stress-strain relationship to EC2.
- Parameters
compressive_strength (
float) – Concrete compressive strengthcompressive_strain (
float) – Strain at which the concrete stress equals the compressive strengthultimate_strain (
float) – Concrete strain at failuren (
float) – Parabolic curve exponentn_points (
int, default:10) – Number of points to discretise the parabolic segment of the curve
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import EurocodeParabolicUltimate
EurocodeParabolicUltimate(
compressive_strength=40,
compressive_strain=0.00175,
ultimate_strain=0.0035,
n=2,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
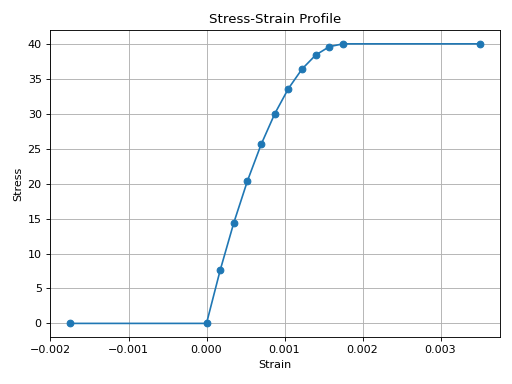
EurocodeParabolicUltimate Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.3. Steel Stress-Strain Profiles#
1.2.3.1. Generic Steel Profile#
- class SteelProfile(strains, stresses, yield_strength, elastic_modulus, fracture_strain)[source]
Bases:
StressStrainProfileAbstract class for a steel stress-strain profile.
- Parameters
strains (
List[float]) – List of strains (must be increasing or equal)stresses (
List[float]) – List of stressesyield_strength (
float) – Steel yield strengthelastic_modulus (
float) – Steel elastic modulusfracture_strain (
float) – Steel fracture strain
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import SteelProfile
SteelProfile(
strains=[-0.05, -0.03, -0.02, -500 / 200e3, 0, 500 / 200e3, 0.02, 0.03, 0.05],
stresses=[-600, -600, -500, -500, 0, 500, 500, 600, 600],
yield_strength=500,
elastic_modulus=200e3,
fracture_strain=0.05,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
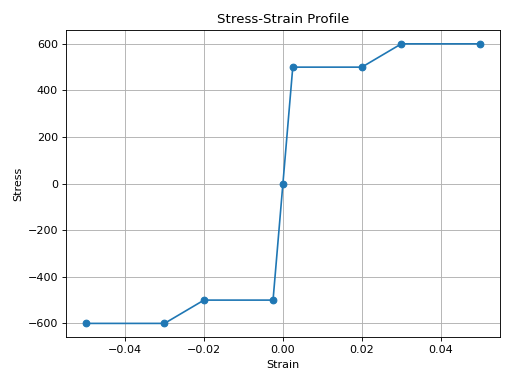
SteelProfile Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.3.2. Elastic-Plastic Steel Profile#
- class SteelElasticPlastic(yield_strength, elastic_modulus, fracture_strain)[source]
Bases:
SteelProfileClass for a perfectly elastic-plastic steel stress-strain profile.
- Parameters
yield_strength (
float) – Steel yield strengthelastic_modulus (
float) – Steel elastic modulusfracture_strain (
float) – Steel fracture strain
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import SteelElasticPlastic
SteelElasticPlastic(
yield_strength=500,
elastic_modulus=200e3,
fracture_strain=0.05,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
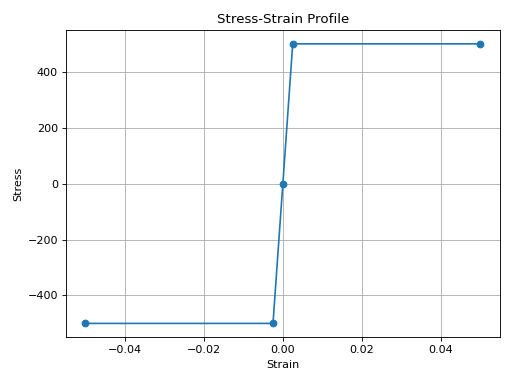
SteelElasticPlastic Stress-Strain Profile#
1.2.3.3. Elastic-Plastic Hardening Steel Profile#
- class SteelHardening(yield_strength, elastic_modulus, fracture_strain, ultimate_strength)[source]
Bases:
SteelProfileClass for a steel stress-strain profile with strain hardening.
- Parameters
yield_strength (
float) – Steel yield strengthelastic_modulus (
float) – Steel elastic modulusfracture_strain (
float) – Steel fracture strainultimate_strength (
float) – Steel ultimate strength
from concreteproperties.stress_strain_profile import SteelHardening
SteelHardening(
yield_strength=500,
elastic_modulus=200e3,
fracture_strain=0.05,
ultimate_strength=600,
).plot_stress_strain()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
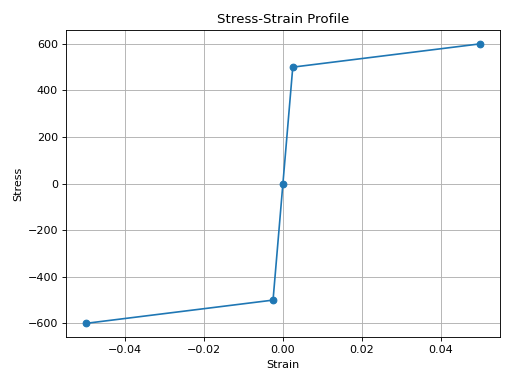
SteelHardening Stress-Strain Profile#