Design Codes#
The design code module allows concreteproperties to be easily used in the context of common reinforced concrete design standards. concreteproperties currently supports the following design codes:
AS 3600:2018#
- class AS3600[source]
Design code class for Australian standard AS 3600:2018.
Inits the AS3600 class.
Using the AS 3600:2018 design code starts by creating an
AS3600 object:
from concreteproperties.design_codes import AS3600
design_code = AS3600()
After a ConcreteSection object has been
created it must be assigned to the design code:
design_code.assign_concrete_section(concrete_section=concrete_section)
- AS3600.assign_concrete_section(concrete_section: ConcreteSection)[source]
Assigns a concrete section to the design code.
- Parameters
concrete_section (
ConcreteSection) – Concrete section object to analyse
Note
To maintain unit consistency, the cross-section dimensions should be entered in [mm].
Creating Material Properties#
The AS3600 class can be used to easily create
material objects whose attributes comply with the standard.
- AS3600.create_concrete_material(compressive_strength: float, colour: Optional[str] = 'lightgrey') Concrete[source]
Returns a concrete material object to AS 3600:2018.
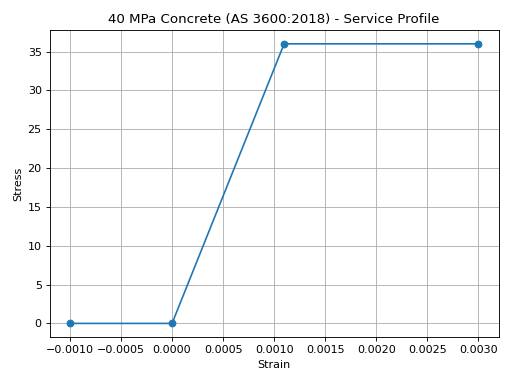
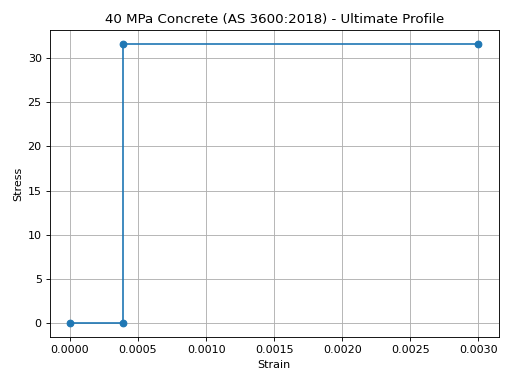
Material assumptions:- Density: 2400 kg/m3- Elastic modulus: Interpolated from Table 3.1.2- Service stress-strain profile: Linear with no tension, compressive strength at 0.9 * f’c- Ultimate stress-strain profile: Rectangular stress block, parameters from Cl. 8.1.3- Alpha squash: From Cl. 10.6.2.2- Flexural tensile strength: From Cl. 3.1.1.3- Parameters
compressive_strength (float) – Characteristic compressive strength of concrete at 28 days in megapascals (MPa)
colour (Optional[str]) – Colour of the concrete for rendering
- Raises
ValueError – If compressive_strength is not between 20 MPa and 100 MPa.
- Returns
Concrete material object
- Return type
from concreteproperties.design_codes import AS3600
design_code = AS3600()
concrete = design_code.create_concrete_material(compressive_strength=40)
concrete.stress_strain_profile.plot_stress_strain(
title=f"{concrete.name} - Service Profile"
)
concrete.ultimate_stress_strain_profile.plot_stress_strain(
title=f"{concrete.name} - Ultimate Profile"
)
- AS3600.create_steel_material(yield_strength: Optional[float] = 500, ductility_class: Optional[str] = 'N', colour: Optional[str] = 'grey') Steel[source]
Returns a steel material object.
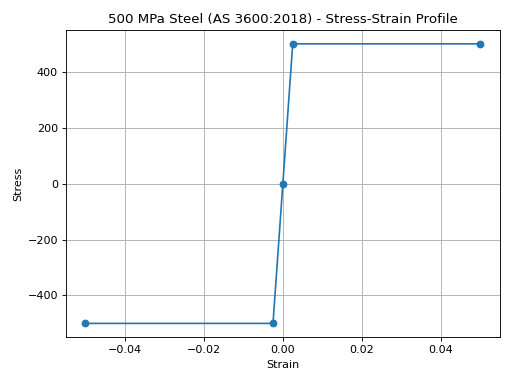
Material assumptions:- Density: 7850 kg/m3- Elastic modulus: 200,000 MPa- Stress-strain profile: Elastic-plastic, fracture strain from Table 3.2.1- Parameters
yield_strength (Optional[float]) – Steel yield strength
ductility_class (Optional[str]) – Steel ductility class (“N” or “L”)
colour (Optional[str]) – Colour of the steel for rendering
- Raises
ValueError – If ductility_class is not N or L
- Returns
Steel material object
- Return type
from concreteproperties.design_codes import AS3600
design_code = AS3600()
steel = design_code.create_steel_material()
steel.stress_strain_profile.plot_stress_strain(
title=f"{steel.name} - Stress-Strain Profile"
)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
Calculating Section Properties#
Analysis methods can be called from the AS3600
object similar to ConcreteSection object.
The following methods are identical to those found in the
ConcreteSection object, i.e. do not apply
any capacity reduction factors:
The following methods have been modified for AS 3600:2018, with codified capacity reduction factors applied.
- AS3600.ultimate_bending_capacity(theta: Optional[float] = 0, n: Optional[float] = 0, phi_0: Optional[float] = 0.6) Tuple[res.UltimateBendingResults, res.UltimateBendingResults, float][source]
Calculates the ultimate bending capacity with capacity factors to AS 3600:2018.
- Parameters
theta (Optional[float]) – Angle (in radians) the neutral axis makes with the horizontal axis (\(-\pi \leq \theta \leq \pi\))
n (Optional[float]) – Net axial force
phi_0 (Optional[float]) – Compression dominant capacity reduction factor, see Table 2.2.2(d)
- Returns
Factored and unfactored ultimate bending results objects, and capacity reduction factor (factored_results, unfactored_results, phi)
- Return type
Tuple[
UltimateBendingResults,UltimateBendingResults, float]
- AS3600.moment_interaction_diagram(phi_0: Optional[float] = 0.6, **kwargs) Tuple[res.MomentInteractionResults, res.MomentInteractionResults, List[float]][source]
Generates a moment interaction diagram with capacity factors to AS 3600:2018.
- Parameters
phi_0 (Optional[float]) – Compression dominant capacity reduction factor, see Table 2.2.2(d)
kwargs – Keyword arguments passed to
moment_interaction_diagram()
- Returns
Factored and unfactored moment interaction results objects, and list of capacity reduction factors (factored_results, unfactored_results, phis)
- Return type
Tuple[
MomentInteractionResults,MomentInteractionResults, List[float]]
- AS3600.biaxial_bending_diagram(n: Optional[float] = 0, n_points: Optional[int] = 48, phi_0: Optional[float] = 0.6) Tuple[res.BiaxialBendingResults, List[float]][source]
Generates a biaxial bending with capacity factors to AS 3600:2018.
- Parameters
n (Optional[float]) – Net axial force
n_points (Optional[int]) – Number of calculation points between the decompression
phi_0 (Optional[float]) – Compression dominant capacity reduction factor, see Table 2.2.2(d)
- Returns
Factored biaxial bending results object and list of capacity reduction factors (factored_results, phis)
- Return type
Tuple[
BiaxialBendingResults, List[float]]
See also
For an application of the use of the design code object, see the example Design Codes.